 COA COA |
 MSDS MSDS |
 HPLC HPLC |
 NMR NMR |
| CAS No: | 164656-23-9 |
| Molecular formula(MF) | C27H30F6N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight(MW): | 528.53 |
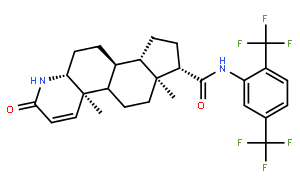
| Alias | (5alpha,17beta)-n-{2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}-3-oxo-4-azaandrost-l-ene-17-carboxamide; (4aR,6aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-N-[2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4a,6a-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide; (4aR,4bS,6aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-N-[2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4a,6a-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide; (4aR,6aS,7S)-N-[2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4a,6a-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide |
| In vitro | DMSO | 62 mg/mL (117.3 mM) |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | 6 mg/mL (11.35 mM) | |
| Water | <1 mg/mL | |
| In vivo |
| Description | Dutasteride is a dual 5-α reductase inhibitor that inhibits conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). | |
|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
|
| In vitro |
Dutasteride inhibits type-1 5AR and type-2 5AR with IC50 of 6 nM and 7 nM, respectively. Dutasteride is 60-fold more potent than Finasteride in its initial Ki versus type 1 5AR and ~5-fold more rapid in inactivating the enzyme. [1] Dutasteride inhibits (3)H-T conversion to (3)H-DHT and, as anticipated, inhibits T-induced secretion of PSA and proliferation in LNCaP cells. Dutasteride also inhibits DHT-induced PSA secretion and cell proliferation with IC50 of 1 μM in LNCaP cells. Dutasteride competes for binding the LNCaP cell AR with an IC50 of 1.5 μM. Dutasteride (10–50 μM) results in enhanced cell death, possibly by apoptosis, in steroid-free medium. [2] Dutasteride reduces cell viability and cell proliferation in androgen-responsive (LNCaP) and androgen-unresponsive (DU145) human prostate cancer(PCa) cell lines. Dutasteride results in overexpressed genes included genes encoding for proteins involved in biosynthesis and metabolism of androgen (HSD17B1;HSD17B3;CYP11B2), androgen receptor and androgen receptor co-regulators (AR;CCND1), and signal transduction(ERBB2; V-CAM; SOS1) whereas, underexpressed genes (KLK3; KLK2; DHCR24) are androgen-regulated genes (ARGs) in androgen-responsive (LNCaP) cell. [3] Dutasteride inhibits FASN mRNA, protein expression and enzymatic activity in prostate cancer cells. [4] |
|
| In vivo | Dutasteride (100 mg/kg/day) has prostates about half as large as those in intact male rats treated with vehicle alone. Dutasteride is orally bioavailable and because of its mechanism of action it easily overcomes the potential liability of being >99% plasma protein bound. [1] |